Open Journal of Orthopedics and Rheumatology
Fibromyalgia (FM): The Effectiveness of the "Perrotta Fibromyalgia Protocol" (PF-p) and the New Possible Etiology of the Clinical Condition. A Pilot Study
Universitas Mercatorum, Rome, Italy (IT)
Author and article information
Cite this as
Perrotta G. Fibromyalgia (FM): The Effectiveness of the "Perrotta Fibromyalgia Protocol" (PF-p) and the New Possible Etiology of the Clinical Condition. A Pilot Study. Open J Orthop Rheumatol. 2025; 10(1): 005-020. Available from: 10.17352/ojor.000051
Copyright License
© 2025 Perrotta G. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Introduction: Fibromyalgia is considered to be a multifactorial idiopathic disease with a strong psychological impact, and no structured protocol is currently able to organize the clinical investigation of the patient, outside of the patient's history, without incurring diagnostic errors.
Objective: The effectiveness of the "Perrotta Fibromyalgia Protocol" (PF-p) is under discussion for the functional diagnosis of patients with fibromyalgia.
Materials and methods: A population sample was selected for the pilot study, which was administered a clinical interview based on narrative-anamnestic and documentary evidence, including key inflammatory indices and Section A of the Perrotta Integrative Clinical Interviews (PICI-3TA), investigating dysfunctional personality traits. Blood investigations needed to complete the individual profile were then performed. Finally, blood indices were repeated after 6 months to evaluate the effectiveness of the protocol used (PF-p).
Results: Preliminary results of clinical interviews and clinical data would suggest that the diagnostic framing might be contaminated by diagnostic errors, partly due to the framing of all clinical symptoms stated by the patients in the selected population sample (n = 48, M = 36.9, SD = 12.6). Blood results confirm the organic inflammatory state. The use of the PF-p, 6 months after the first instrumental verification, shows a marked and significant alleviation of symptoms in 72.9% of cases (35/48) and complete resolution in 27.1% of cases (13/48).
Conclusions: Fibromyalgia could be considered a polysymptomatic condition (and not an independent disorder or disease) resulting from an active systemic inflammatory state capable of interfering with normal organic functioning, capable of altering one or more biological functions.
Indexing and Abstracting
" target="_blank"> %29&highlight=1" target="_blank"> '&sort=relevance" target="_blank"> &clusterAbbreviations and Abbreviationss=on&scope=" target="_blank"> &clusterAbbreviations and Abbreviationss=true&expandSearch=on&translateSearch=off#/oclc/8654690991" target="_blank"> " target="_blank"> " target="_blank"> '&clusterResults=true" target="_blank"> " target="_blank">
FM: Fibromyalgia; FMS: Fibromyalgia Syndrome; HLA: Human Leukocyte Antigen; CFS: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome; MCS: Multiple Chemical Sensitivity; SFB: Benign Fasciculations Syndrome or Benign Fasciculations Syndrome
Introduction
Definition and epidemiological data
Fibromyalgia (FM) or Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is a multifactorial idiopathic disorder of a genetically based inflammatory nature, with clinical manifestations of immunoreumatic, neurologic, psychiatric, muscular, and metabolic types [1-3]. The first description of FM is found in the nineteenth century. The term “fibrositis”, which Gowers first used in 1904, was in use until the 1970s and 1980s, when a central nervous system-related etiology was proposed. In 1950, Graham described fibrositis as a “pain syndrome” in the absence of a specific organic disease. Then, in the middle of the 1970s, Smythe and Moldofsky created the new term “fibromyalgia” and named the so-called “tender points” regions of extreme tenderness. The American College of Rheumatology committee’s widely used diagnostic standards, which were only recently modified, were not developed until 1990 [4]. It mainly arises in the female sex and adulthood (second to fifth decades, peaking around 25-35 years and 45-55 years), although there are cases of Fibromyalgia in pediatric age or during adolescence, albeit rare. Its prevalence in the adult general population is 0.5% in males and 3.5% in females, while other studies delimit it at 2% - 8% of the population, with a female-to-male incidence between 7:1 and 9:1, whereas in the pediatric population, the incidence is significantly lower, around 0.2% - 0.6% on average [5-8].
Etiological causes
It is known that fibromyalgia is caused by a central sensitization phenomenon characterized by dysfunction of neurological circuits, involving the perception, transmission, and processing of afferent nociceptive stimuli, with a prevalent manifestation of pain at the level of the musculoskeletal system [9]. The most accepted etiologic cause that is described in the literature is FM as a multifactorial idiopathic disorder [10-14], but there are alternative hypotheses defining it as a neurotically based psychiatric disorder [15-17], a neurometabolic disorder [18-24], a neurovascular and muscular disorder [25], or a neuroinflammatory disorder [26-30], up to the possible atypicality of an already known disorder. However, all alternative hypotheses can be traced back to a systemic inflammatory process that triggers the dysfunctional mechanism (e.g., the serotonin deficiency found in Fibromyalgia patients could be traced back to a gut dysbiotic process where 90% of serotonergic production occurs). The physical trauma of a musculoskeletal nature, psychological trauma, bacterial or viral infection, celiac disease (and/or gluten sensitivity), autoimmune disorders, allergies, neuropathy, mitochondrial alterations, gut dysbiosis, and various genetic polymorphisms (e.g. HLA A*29 and B*44, 102T/C of the 5-HT2A receptor, ADRB2, ADRA1A, COMT rs4818, and MAO-A allele3) are considered to date to be triggering or otherwise favoring causes of FM activation [31-41].
fMRI images
In the literature, studies that have examined fMRI images associated with various pain thresholds in fibromyalgia patients have found increased cortical blood flow in areas of the brain associated specifically with pain processing, with lower stimulation in FM subjects. They also found reduced connectivity in the descending pain modulation system, particularly from the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) to the amygdala, hippocampus, and brainstem, and it is precisely the ACC, periaqueductal gray, and ventromedial rostral medulla that appear to be large components of the descending pain processing pathway [4].
Critical profiles
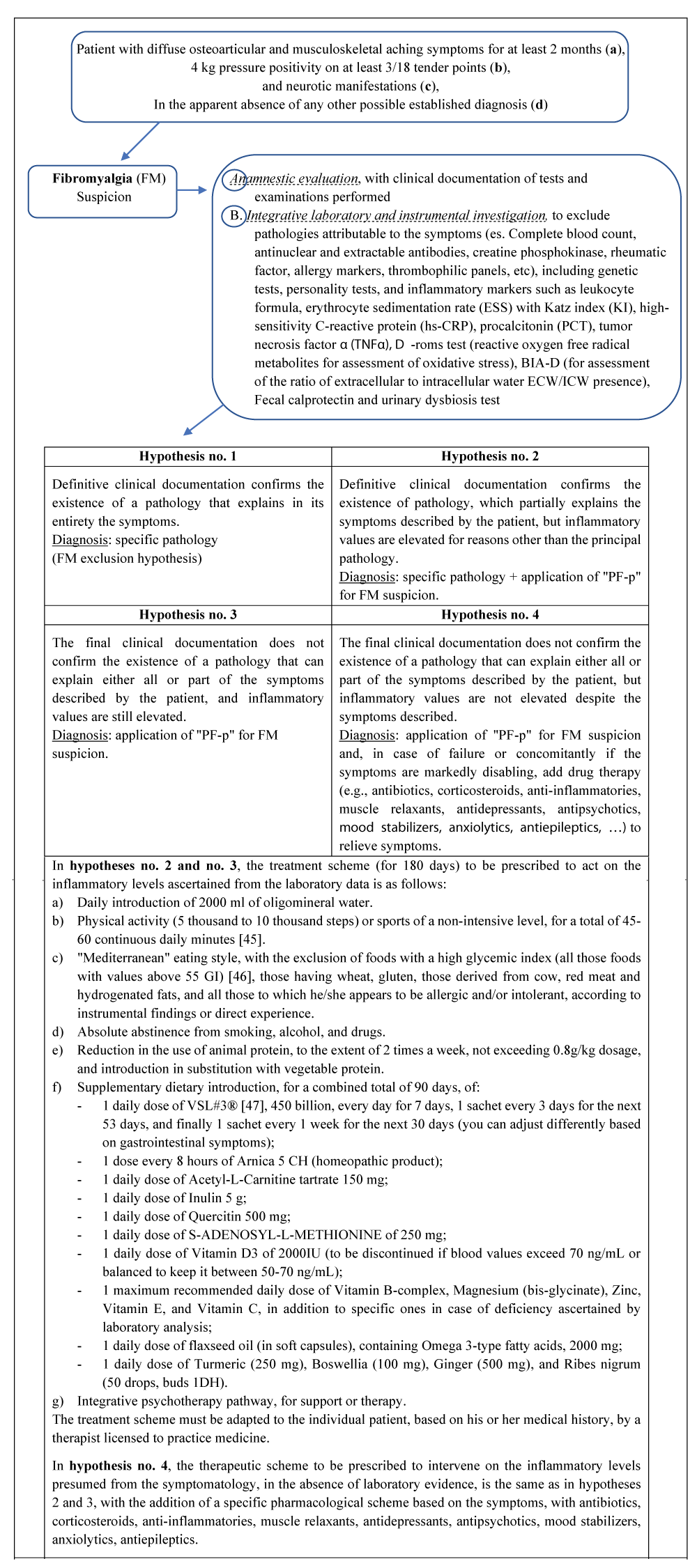
The definition of FM is relatively recent and continues to be referred to as a controversial diagnosis or, at any rate, an umbrella term encompassing a heterogeneous multitude of symptoms, which vary over time based on changing factors. It seems clear that the difficult nosographic placement (a), the selection of the population often numerically insufficient to reach the representativeness necessary to be able to consider the results of the studies reasonably functional to the objectives of the research (b), the heterogeneity of the symptoms among them not coherently connected according to a logical continuum (c), the absence of a precise and shared diagnostic pathway independently and not according to the logic of exclusion (d), the absence of one or more specific markers (e.g., the prostate-specific antigen in prostate cancer) or an instrumental test (e.g., blood eosinophil count in allergic reactions or electromyography in muscle disease) that can place the diagnosis with certainty (e), the still controversial and ill-defined role of cytokines in patients diagnosed with FM (f), the significant impact of stressors on the perceptual state of the algic symptoms (g) and the lability of the symptoms, which tend to change over time without a defined gravitational or progressive pattern (h), are all elements that might argue for a downsizing of the evaluative framework of this disorder. Bearing in mind that the symptomatology is markedly somatic and not otherwise explicable except in an atypical or otherwise framed condition, it seems more likely that Fibromyalgia can and should be considered as the active manifestation of a systemic inflammatory state capable of interfering with normal organic functioning and alternating one or more biological functions, resulting in the symptomatological consequence often described by patients but not framed in a precise nosographic framework. The symptomatological manifestation of the psychological and psychiatric matrix suggests that the somatic component in the patient plays a central role, both in interpretative and therapeutic [42].
Fibromyalgia classification currently shared
The current classification in the literature [43] recognizes 4 principal different forms of FM based on the criterion of pain and psychiatric symptoms (a. extreme sensitivity to painful stimuli but without associated psychiatric conditions; b. Fibromyalgia with comorbid psychiatric symptoms, depression with pain; c. major depression with concomitant Fibromyalgia syndrome; d. Fibromyalgia due to somatization. The reductionism of the model, the absence of a diagnostic protocol, and the lack of applicative adherence to the clinical hypotheses of the alleged FM were the reasons that fueled the need to propose some correctives to the current knowledge on the subject (included in the "Materials and methods" section).
Study objectives
Having ascertained the clinical need to provide better nosographic framing for patients diagnosed with FM, the present research work pursues the primary objective of structuring through the development of a new theory, a new model and a new protocol ("Perrotta Fibromyalgia Protocol", PF-p) the best clinical framing of the patient, while as secondary objectives it pursues the evaluation of the outcomes resulting from the application of these innovations and the comparison with the outcomes already obtained from previous clinical findings, identified in the literature.
Materials and methods
Study methods
Starting from the classic definition of “Fibromyalgia”, a population sample for the pilot study was selected for the administration of the following clinical instruments:
- Clinical interview, based on narrative-anamnestic and documentary evidence;
- Outcome analysis of key inflammatory indices (and any doctor's prescription to perform missing clinical blood tests);
- Administration of Section A of the Perrotta Integrative Clinical Interviews (PICI-3TA) [27], to investigate the patient's dysfunctional personality traits.
The phases of the research (methods) were divided as follows:
- selection of the population sample, according to the parameters indicated in the following paragraph;
- drafting materials structuring the theory (PF-t) (Table 1), model (PF-m) (Table 1), and protocol (PF-p) (Table 2) of the newly proposed;
- analysis of past medical records, with a request for supplementation of specific blood tests (Table 3) if not possessed or not recent (older than 60 days), at laboratories certified by the National Health System;
- administration of Section A of the Perrotta Integrative Clinical Interviews (PICI-3TA), to investigate the patient's dysfunctional personality traits;
- administration of the new protocol (PF-p), with the attached integrated dietary plan, lasting 6 months (180 days) and rechecking of the blood indices prescribed in step 3 within the following week;
- clinical interview, for the assessment of outcomes;
- data processing following administration;
- Comparison of data obtained.
Setting and participants
The inclusion criteria for admission to the study population sample are:
- Age between 14 years and 65 years, m/f defined as Italian nationality by birth, with both parents of Italian origin.
- The medical diagnosis of Fibromyalgia (FM) is made based on clinical documentation certified by public hospital institutions or private facilities conventional with the Italian National Health System, with a medical report initialed by a licensed therapist and practicing medical specialist.
- Persistent symptoms of Fibromyalgia, undergoing drug therapy for at least 2 months.
- Complete suspension of drug therapy, with medical advice, according to the protocol of the specific drug and at least 1 month before PF-p administration.
The exclusion criteria are:
- Age under 14 years old, due to lack of participation in the selection process, and over 65 years old, as of this age range, by their nature, they may be prone to neurodegenerative and/or neurovascular medical conditions or with difficult-to-manage complications that could compromise the proper process of identifying diagnosis and treatment.
- Subjects undergoing sexual gender transition or with completed pathways.
- Non-Italian nationality or otherwise with non-Italian parents.
- Absence of diagnosis of Fibromyalgia made by a therapist practicing in the medical profession, even in the presence of active symptoms.
- Presence of severe Fibromyalgia symptoms (with subjective algic perceptual rating of 9-10 on a 0-10 scale).
- Drug therapy is active or inactive for less than 1 month or discontinued without a specialist medical indication.
The absence of a control group is foreseen by the study and is not a limitation, as the blood tests are carried out on the basis of a diagnosis of fibromyalgia; therefore, the absence of this diagnosis is a cause for exclusion and the non-existence of the investigation.
The setting is chosen, taking into account the protracted pandemic period (already in progress since the beginning of the present research) and cost-effectiveness, is the online platform via Skype and WhatsApp video call, both for the clinical interview and for the subsequent stages. The present research work was carried out from February 2020 to February 2024, using a sample population already selected for other studies, adding additional participants through online announcements on social platforms and websites dedicated to the topic of Fibromyalgia.
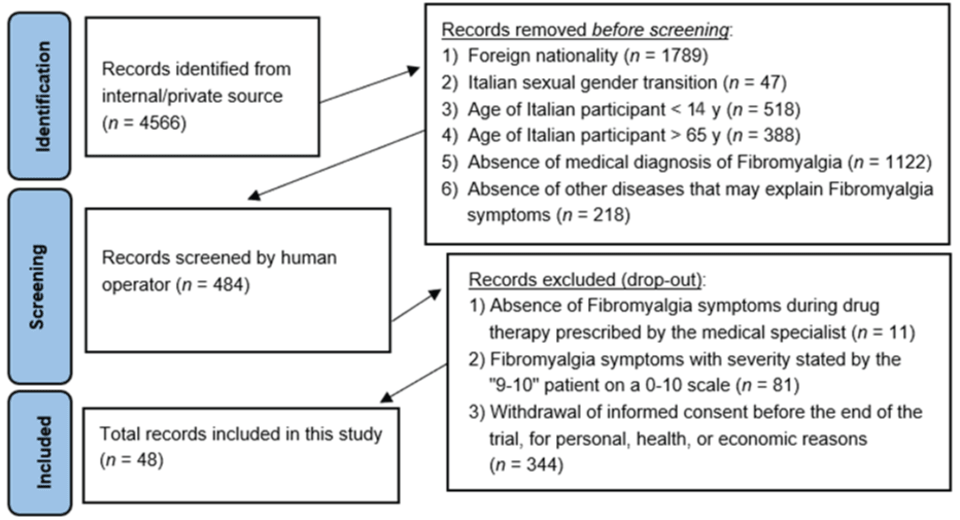
The selected population sample, which met the requirements for inclusion in the study, was 484 participants, but the individual economic cost to be incurred to perform the supplementary and integrative tests, and those in follow-up, and the purchase of dietary supplements along with the expense of doctor's visits, reduced the number to 48 participants (drop-out = 90%) (Figure 1), which definitively ended the present study.
The final population sample was divided as follows progressive number of participants and by age of birth (Table 4).
The absence of a control group in this pilot study is determined by the research objective, which is to evaluate the efficacy of PF-p in the adolescent, adult, and mature fibromyalgia population, and not in the healthy population.
Data collection and definition of variables
Clinical data, such as gender, age, body mass index, leukocyte formula (a), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESS) (b) with Katz index (KI) (c), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) (d), procalcitonin (PCT) (e), tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) (f), D-roms test (reactive oxygen free radical metabolites for assessment of oxidative stress) (g), BIA-D (for assessment of the ratio of extracellular to intracellular water ECW/ICW presence) (h), fecal calprotectin (i) and urinary dysbiosis test (j), were collected from the medical records. Normal blood and urinary parameters were established according to the indications of the laboratory that performed the investigations. Psychiatric data of neurotic, dramatic, and psychotic profiles were collected using the PICI-3.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 28). Categorical variables are presented as frequencies and percentages, and continuous variables are reported as mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile ranges (IQR). T-tests were conducted for dependent and independent data. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables between the groups. Categorical variables were compared using the Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Having selected the population sample based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria and concluded the phase of drafting the materials, including it in the informed consent and data processing, we proceeded to the receptive phase of the participants, with the receipt of clinical documentation and preliminary clinical interview. Having collected all the necessary anamnestic data, psychological data by administering the PICI-3TA and those from the suggested supplementary blood investigations carried out at laboratories certified by the National Health System, the exact quantitative numerical size of the final population sample [n = 48 (14-65y), M = 36.9, SD = 12.6] was compiled, and the results were written (Tables 5-7).
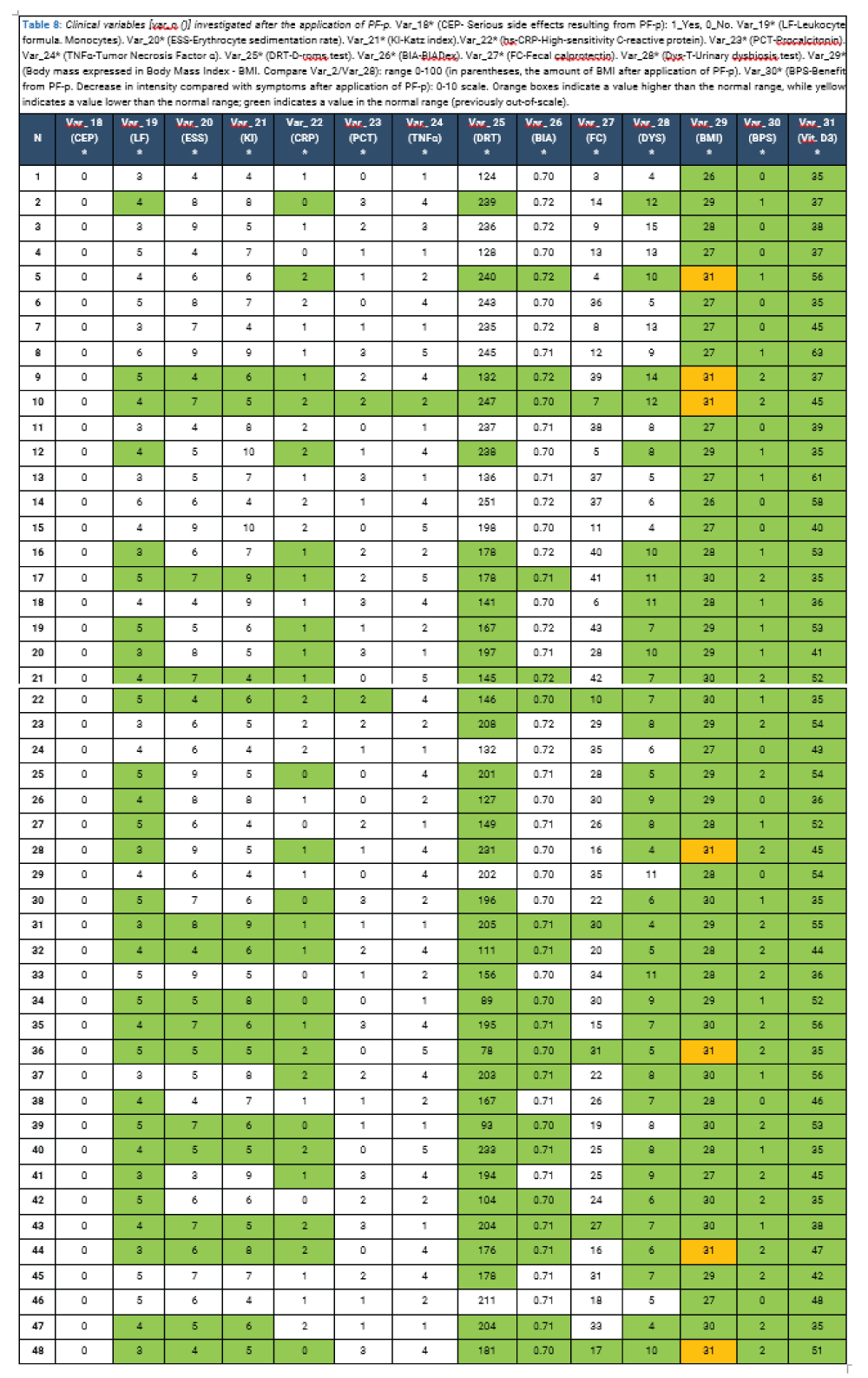
The final sample population was thus educated, via online clinical interview, on the practical application of the PF-p, particularly for the purchase of necessary supplementary products, to be taken in the following semester. Upon completion, within 2 weeks, the blood tests covered by the study variables were requested (Tables 8).
Following the application of the PF-p to the selected population sample, and subsequent control of the variables investigated, it appears that each variable altered in value and out of scale has receded, with the attenuation of symptomatology suffering the total absence of clinically relevant manifestations (Tables 9).
Data on var_6 (PSY) were obtained by administration of the PICI-3TA (Section A), which in detail detects for 85.4% (41/48 participants) a dysfunctional personality picture of predominantly neurotic type, while for the remaining 14.6% (7/48 participants) a predominantly dramatic-psychotic picture emerges [64,65] (Tables 10).
Discussions
Preamble
The results clearly and systematically highlight the efficacy of the protocol on patients diagnosed with FM, retrospectively excluding patients with extreme subjective pain (9-10 on the 0-10 scale), as none of them was able to complete the study for economic reasons (the costs to themselves too high, relative to doctor visits and supplementary tests) and clinical reasons (the disabling symptomatology forced the patient to discontinue therapy in favor of pharmacological therapy, and this compromised the results). Data analyzed by age range show that patients aged between 14 and 34 years have a clinical picture that cannot justify the symptoms, while the remaining groups show clear indices of inflammation; data, however, were not analyzed by sex because the comparison sample is too small. The following paragraphs are about comparing data of variables with out-of-range values.
Comparison of Var_2 (BMI) and Var_29 (BMI)-x*
Var_2 refers to subjective body mass values expressed in Body Mass Index (BMI) recorded on the previous day, about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 27-34 (thus, 100% of the sample population found to be overweight or obese). Var_29*, related to the previous one, refers to the subjective body mass values expressed in Body Mass Index (BMI) recorded on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 26-31 (thus, with 95.8% of the population sample found to be overweight and only 4.2% found to be obese) and with a decrease of 1 to 4 BMI points compared with the data before the protocol was applied. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, in the final population sample, the variable "body mass" appears to be significantly related to the recorded inflammatory status and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol. At the follow-up clinical interview, it was reported by 89.5% of patients with a value of 2 in Var_29* (17/19) that the protocol was not executed perfectly and that there were several (unreported) oversights in both the execution of the dietary plan (sporadic introduction of gluten and cow's milk derivatives) and the administration of the supplementary treatment plan; despite this, however, there were clear improvements from the previous clinical position.
Comparison of Var_5 (CED) and Var_18 (CEP)*
Var_5 refers to the presence of the side effects of the drug therapy administered before entering the population sample, recorded on the previous day at the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle. Var_18, related to the previous one, refers to the presence of the side effects of protocol administration, recorded from the day after the end of the quarterly PF-p cycle. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, to the final population sample, in 100% of cases (48/48) the protocol application has no side effects of any kind, in contrast to variable No. 5, which captures 100% of positive responses to the question of whether or not serious side effects have been experienced since the administration (predominantly, aggravation of psychiatric symptoms of a mood and anxiety nature, hypomanic episodes, apathy and decreased sexual desire, but also gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation and abdominal bloating). The comparison of these two variables must then be parameterized to another significant finding, related to Var_6 on the presence or absence of psychiatric symptoms before the administration of the protocol and detected by administration of the PICI-3TA (Section A): in fact, the survey produced the result of 100% of the sample having a dysfunctional personality profile, and with 85.4% (41/48) of the neurotic type, with greater prevalence for the anxiety-somatic structure and some dramatic and psychotic elements related to resistant dysfunctional personality traits [65-69].
Comparison of Var_7 (LF) and Var_19 (LF)*
Var_7 refers to the lymphocyte survey and the exact quantification of its components, recorded on the previous day about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with normal minimum-maximum values of 3-8% for monocytes (in fact, the latter are the only ones to be out of scale, with 62.5% of the population sample). Var_19*, to the previous one, refers to the same survey but recorded on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with the same scaled values (but all returned and normalized, according to the reference range). A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, in the final population sample, the variable "leukocyte-like monocytes" appears to be significantly related to the recorded inflammatory status and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_8 (ESS) and Var_20 (ESS)*
Var_8 refers to the quantification of erythrocyte sedimentation rate according to a normal range of 0-15 mm/h for men and 0-20 mm/h for women, recorded on the previous day about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 8-27 (with 33.3% of the population sample on values >20 mm/h). Var_20*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, in the final population sample, the variable "erythrocyte sedimentation rate" appears to be significantly related to the recorded inflammatory status and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_9 (KI) and Var_21 (KI)*
Var_9 refers to the quantification of the Katz index according to a normality range of 4-10 for men and 4-15 for women, recorded on the previous day about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 6-9 for men and 6-23 for women (with 33.3% of the female population sample on values >15 mm/h). Var_21*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, to the final population sample, the variable "Katz" appears to be significantly related to the inflammatory status recorded in the female population and to the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_10 (CRP) and Var_22 (CRP)*
Var_10 refers to high-sensitivity C-reactive protein quantification according to a normality range of 0-3 mg/L, recorded the previous day, about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 1-9 (with 41.7% of the population sample on values > 3 mm/h). Var_22*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, in the final population sample, the variable "high-sensitivity c-reactive protein" appears to be significantly correlated with the recorded inflammatory status and improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_11 (PCT) and Var_23 (PCT)*
Var_11 refers to the quantification of procalcitonin according to a normal range of < 0.05 ng/ml, recorded on the previous day, about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 0.03-0.08 (with 4.2% of the population sample on values > 0.05 ng/ml). Var_23*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. Comparison of these 2 variables shows that, to the final population sample, the variable "procalcitonin" appears to be significantly related to the recorded inflammatory status and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol; however, taking into account the smallness of the sample (1/48) it is a value that may not have clinical relevance.
Comparison of Var_12 (TNFα) and Var_24 (TNFα)*
Var_12 refers to the quantification of "tumor necrosis factor α" according to a normality range < 8 pg/ml, recorded on the previous day about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 2-14 (with 2.1% of the population sample on values > 8 mm/h). Var_24*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, to the final population sample, the variable "tumor necrosis factor α" appears to be significantly related to the recorded inflammatory state and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol; however, taking into account the smallness of the sample (1/48), it is a value that may not have clinical relevance.
Comparison of Var_13 (DRT) and Var_24 (DRT)*
Var_13 refers to the quantification of the D-roms test according to a normality range < 300 U/CARR, recorded on the previous day, about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 260-528 (with 72.9% of the population sample on values > 300 U/CARR). Var_24*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that, to the final population sample, the variable "D-roms test" appears highly suggestive of being significantly related to the recorded inflammatory status and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_14 (BIA) and Var_25 (BIA)*
Var_14 refers to the quantification of BIA according to a normality range of 0.7-0.75 (ECW/ICW), recorded on the previous day about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 0.71-0.97 (with 39.6% of the population sample on values > 0.75). Var_25*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the end of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that in the final population sample, the variable "BIA" appears to be significantly related to the recorded inflammatory status and the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_15 (FC) and Var_27 (FC)*
Var_15 refers to the quantification of fecal calprotectin according to a normal range of < 50 µg/g, recorded the previous day, about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 2-103 (with 12.5% of the population sample on values > 50 µg/g). Var_27*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these 2 variables shows that in the final population sample, the variable "fecal calprotectin" appears to be significantly correlated with the recorded inflammatory status and with the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol. Specifically, all 6 patients who were positive for this marker had marked and disabling intestinal symptoms (gastroesophageal reflux, chronic gastritis, chronic constipation, bacterial overpopulation syndrome, and irritable bowel syndrome) that did not resolve with drug therapy but improved with protocol application.
Comparison of Var_16 (DYS) and Var_28 (DYS)*
Var_16 refers to the quantification of the degree of intestinal dysbiosis according to a normal range of 4 mg - 20 mg, recorded the previous day, about the beginning of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 5-40 (with 70.8% of the population sample on values > 20 mg). Var_28*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. A comparison of these two variables shows that, in the final population sample, the variable "dysbiosis test" appears to be significantly correlated with the recorded inflammatory status and with the improvement in general health status following the application of the protocol. Specifically, all 34 patients who were positive for this test had mild to moderate intestinal symptoms that resolved only partially with drug therapy but improved markedly until they disappeared almost completely with the application of the protocol.
Comparison of Var_17 (DYS) and Var_31 (DYS)*
Var_17 refers to the quantification of plasma Vitamin D3 levels according to a normal range of 30-100 ng/ml, recorded the day before the start of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 6-19 (with 100% of the population sample on values < 20 ng/ml). Var_31*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of the same recorded, however, on the day after the end of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values all falling within the normal range. Comparison of these two variables shows that, in the final population sample, the variable "Vit. D3" appears to be significantly correlated with the recorded inflammatory status and with the improvement in general health status following application of the protocol. Specifically, following supplemental administration of this vitamin, all 48 patients reported perceiving a more stable mood, decreased flu episodes, and increased physical resistance to exertion.
Comparison of Var_3 (PSS) and Var_30 (BPS)*
Var_3 refers to the quantification of benefits received from PF-p and more generally the state of algic perception (also intended as disability produced by symptoms) according to a 0-10 scale, recorded on the day before the start of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 3-8 (with 52.1% of the population sample on values 6-8). Var_30*, related to the previous one, refers to the quantification of perceived pain always according to a 0-10 scale recorded on the day after the conclusion of the quarterly PF-p cycle, with minimum-maximum values of 0-3 (thus, significantly lower than the data before the application of the protocol). Symptoms resolved completely in 27.1% of cases (13/48), while they subsided, becoming easily tolerable in the remaining 72.9% of cases (35/48). A comparison of these two variables shows that, to the final population sample, the variable "perceived pain" appears to be significantly correlated with the recorded inflammatory status and improvement in general health status following protocol application.
Comparison of study outcomes with current literature
The outcomes of this research show that fibromyalgia has a clear inflammatory matrix, with an immunological background (based on blood findings related to lipid mediators, some proinflammatory cytokines, direct and indirect markers for oxidative stress, and plasma element research), as reported abundantly in the literature [70-77]. Medium confirmatory findings are given by the presence of intestinal dysbiotic processes, as also confirmed in the literature [38-40,78].
Study limitations and prospects
Although the present pilot study was able to demonstrate the central role of the inflammatory process and the usefulness of the application of the "Perrotta Fibromyalgia Protocol" to manage the fibromyalgic condition, not as an independent nosographic disorder but as a systemic, polysymptomatic inflammatory state, the study was structured with a small population sample, for economic reasons and independent of the investigator, and therefore this research can only be considered a pilot study. Another limitation is determined by the fact that, again for economic reasons, the laboratory analyses were carried out independently, by patients, in different analytical laboratories that therefore use different instrumentation and calibrations; this implies the loss of the accuracy of the analytical findings, which would have been obtained by carrying out all the analyses in the same laboratory. Finally, a final limitation is determined by the fact that the population included in the present study is exclusively of Italian nationality, which limits the generalizability of the results. Future challenges will be to find an adequate and representative population sample, with a multicenter, funded study that can demonstrate whether the results obtained from this pilot study are confirmatory of the goals achieved, with a more structured follow-up over time (at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months of application of the nonpharmacological protocol) and focused on both clinical and psychological and nutritional profiles, also on other blood values (such as those related to coagulation [79] other proinflammatory cytokines, cardiac and brain markers [80]).
Conclusion
The current results obtained from this pilot study have shown that Fibromyalgia can be considered a polysymptomatic condition (and not an independent disorder or disease) resulting from an active systemic inflammatory state, capable of interfering with normal organic functioning, altering one or more biological functions, including psychological (as already demonstrated in the literature, including about the microbiota), thus giving rise to the symptoms described by patients. The symptomatological description of Fibromyalgia is compatible with a multi-inflammatory profile, and therefore it is not necessary to establish a new specific nosography, having instead to discuss the issue of the inflammatory state as a direct cause of the symptoms suffered by patients. The administration of single drugs mitigates the extent but rarely leads to resolution, which is instead achieved by opting for the holistic approach of the “Perrotta Fibromyalgia Protocol” (PF-p), considering the pharmacological approach as a secondary and complementary line in cases of severe, persistent, and complicated symptoms.
Ethics approval and consent to partecipate
This study was waived for ethical review and approval because all participants were assured compliance with the ethical requirements of the Charter of Human Rights, the Declaration of Helsinki in its most recent version, the Oviedo Convention, the guidelines of the National Bioethics Committee, the standards of "Good Clinical Practice" (GCP) in the most recent version, the relevant national and international ethical codes, as well as the fundamental principles of state law and international laws according to the updated guidelines on observational studies and clinical trial studies. For patients under the age of 18 years, specific permission to participate was requested by stipulation of data processing and computer consent from both parents or legal guardians. Under Legislative Decree No. 52/2019 and Law No. 3/2018, this research does not require the prior opinion of an ethics committee, in implementation of Regulation (EU) No. 536/2014 and by Regulation (EU) 2017/745, the Declaration of Helsinki and the Oviedo Convention, since the scientific research contained in the manuscript: (a) does not concern new or already marketed drugs or medical devices; (b) does not involve the administration of a new or already marketed drug or medical device; (c) does not have commercial purposes; (d) is not sponsored or funded; (e) participants have signed the informed consent and data processing, in compliance with applicable national and EU regulations; (f) refers to non-interventional and observational-comparative diagnostic topics; (g) the population sample was collected at a date before the start of this study and is part of a private and non-public database.Informed consent statement
Subjects were recruited who gave regular informed consent and treatment of sensitive data; moreover, these subjects asked and obtained from Giulio Perrotta, as the sole examiner and project manager, not to meet the other study collaborators, thus remaining completely anonymous, finally requesting that only their trusted general practitioner or specialist confirm the absence of dangers to their health from the administration of the supplements included in the protocol, by what was stated in their medical history.
Data availability statement
The subjects who participated in the study requested and obtained that GP be the sole examiner during the therapeutic sessions and that all other authors be aware of the participants' data in an exclusively anonymous form.
The author would like to thank the general and specialist medical personnel involved during the clinical evaluation phase of the protocol and the required laboratory analyses for their cooperation. Thanks are also extended to the technical staff of the analytical laboratories involved, who facilitated the data acquisition process, in compliance with current regulations on data processing and storage.
- Ambrose KR, Gracely RH, Glass JM. Fibromyalgia dyscognition: concepts and issues. Reumatismo. 2012;64(4):206-15. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4081/reumatismo.2012.206
- Perrotta G. Fibromyalgia (FM): Definition, Differential Diagnosis, Clinical Contexts and Therapeutic Approaches. The Recent State of the Medical Art and a Possible Key to Etiological Interpretation. A Narrative Review. Ann Musculoskelet Med. 2025;9(1):001-011.
- NIAMS.NIH.GOV. Fibromyalgia. Available from: niams.nih.gov/health-topics/fibromyalgia.
- Gyorfi M, Rupp A, Abd-Elsayed A. Fibromyalgia Pathophysiology. Biomedicines. 2022;10:3070. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123070
- Todesco S, Gambari PF, Punzi L. Malattie reumatiche. McGraw-Hill Ed.; 2007.
- Chakrabarty S, Zoorob R. Fibromyalgia. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76(2):247-254. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17695569/
- Bartels EM, Dreyer L, Jacobsen S, Jespersen A, Bliddal H, Danneskiold-Samsøe B. Fibromyalgia, diagnosis and prevalence. Are gender differences explainable? Ugeskr Laeger. 2009;171(49):3588-92. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19954696/
- Clauw DJ, Arnold LM, McCarberg BH. The science of fibromyalgia. Mayo Clin Proc. 2011;86(9):907–11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4065/mcp.2011.0206
- Siracusa R, Paola RD, Cuzzocrea S, Impellizzeri D, et al. Fibromyalgia: Pathogenesis, Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3891. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083891
- Gau SY, Leong PY, Lin CL, Tsou HK, Wei JC. Higher Risk for Sjögren's Syndrome in Patients With Fibromyalgia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Front Immunol. 2021;12:640618. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.640618
- Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. Candidate gene studies of fibromyalgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(2):417-26. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1678-9
- Behnoush AH, Khalaji A, Khanmohammadi S, Alehossein P, Saeedian B, Shobeiri P, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in fibromyalgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of its role as a potential biomarker. PLoS One. 2023;18(12):e0296103. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0296103
- Yunus MB. Genetic factors in fibromyalgia syndrome. Z Rheumatol. 1998;57 Suppl 2:61-2. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003930050237
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Lamas JR, Abàsolo L, Baena S, Olano-Martin E, Collado A, et al. The rs3771863 single nucleotide polymorphism of the TACR1 gene is associated to a lower risk of sicca syndrome in fibromyalgia patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33(1 Suppl 88):S33-40. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25786041/
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR®). APA; 2022. Available from: https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm
- Sommer C, Hauser W, Gerhold K, Joraschky P, Petzke F, Tölle T, Uçeyler N, et al. Etiology and pathophysiology of fibromyalgia syndrome and chronic widespread pain. Schmerz. 2008;22(3):267-82. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00482-012-1174-0
- Kudlow PA, Rosenblat JD, Weissman CR, Cha DS, Kakar R, McIntyre RS, Sharma V. Prevalence of fibromyalgia and co-morbid bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2015;188:134-42. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.08.030
- Emad Y, Regab Y, Zeinhom F, El-Khouly G, Abou-Zeid A, Rasker JJ. Hippocampus dysfunction may explain symptoms of fibromyalgia syndrome. A study with single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(7):1371-1377. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18484688/
- Simms RW, Goldenberg DL. Symptoms mimicking neurologic disorders in fibromyalgia syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1988;15(8):1271-1273. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3184073/
- Park DC, Glass JM, Minear M, Crofford LJ. Cognitive function in fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(9):2125-33. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9%3C2125::aid-art365%3E3.0.co;2-1
- Bangert AS, Glass JM, Welsh RC, Crofford LJ, Taylor SF, Park DC. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of working memory in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:S90. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291785932_Functional_magnetic_resonance_imaging_of_working_memory_in_fibromyalgia
- Kuchinad A, Schweinhardt P, Seminowicz DA, Wood PB, Chizh BA, Bushnell MC. Accelerated brain gray matter loss in fibromyalgia patients: premature aging of the brain? J Neurosci. 2007;27(15):4004-7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0098-07.2007
- Wood PB. Role of central dopamine in pain and analgesia. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008;8(5):781-97. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.8.5.781
- Orriols R, Costa R, Cuberas G, Jacas C, Castell J, Sunyer J. Brain dysfunction in multiple chemical sensitivity. J Neurol Sci. 2009;287(1–2):72–8. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2009.09.003
- Albrecht PJ, Hou Q, Argoff CE, Storey JR, Wymer JP, Rice FL. Excessive peptidergic sensory innervation of cutaneous arteriole-venule shunts (AVS) in the palmar glabrous skin of fibromyalgia patients: implications for widespread deep tissue pain and fatigue. Pain Med. 2013;6(14):895-915. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12139
- Bascom R, Meggs WJ, Frampton M, Hudnell K, Killburn K, Kobal G, et al. Neurogenic inflammation: with additional discussion of central and perceptual integration of nonneurogenic inflammation. Environ Health Perspect. 1997;105 Suppl 2:531-7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.97105s2531
- Link AS, Anikó K, Edvinsson L. Treatment of migraine attacks based on the interaction with the trigemino-cerebrovascular system. J Headache Pain. 2008;9(1):5-12. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10194-008-0011-4
- Weglicki WB, Phillips TM. Pathobiology of magnesium deficiency: a cytokine/neurogenic inflammation hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1992;263(3 Pt 2):R734-7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.3.r734
- Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, Camozzi F, Lombardi R, Melli G, et al. The diagnostic criteria for small fiber neuropathy from symptoms of neuropathology. Brain. 2008;131(Pt 7):1912-25. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn093
- Faber CG, Hoeijmakers JGJ, Ahn H-S, Cheng X, Han C, Choi JS, et al. Gain of function Naν1.7 mutations in idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2012;71(1):26-39. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22485
- Rossi A, Di Lollo AC, Guzzo MP, Giacomelli C, Atzeni F, Bazzichi L, et al. Fibromyalgia and nutrition: what news? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33(1Suppl 88):S117–25. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25786053/
- Caro XJ, Winter EF. The Role and Importance of Small Fiber Neuropathy in Fibromyalgia Pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2015;19(12):55. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-015-0527-7
- Klein CJ, Lennon VA, Aston PA, McKeon A, Pittock SJ. Chronic pain as a manifestation of potassium channel-complex autoimmunity. Neurology. 2012;79(11):1136-44. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0b013e3182698cab
- Sánchez-Domínguez B, Bullon P, Román-Malo L, Marín-Aguilar F, Alcocer-Gómez E, Carrión AM, et al. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and, inflammation common events in skin of patients with Fibromyalgia. Mitochondrion. 2015;21:69-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2015.01.010
- Isasi C, Colmenero I, Casco F, Tejerina E, Fernandez N, Serrano-Vela JI, et al. Fibromyalgia and non-celiac gluten sensitivity: a description with remission of fibromyalgia. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(11):1607-12. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-2990-6
- Tzatha E, Chin RL. Small fiber abnormalities in skin biopsies of patients with benign fasciculations. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2014;16(1):12-4. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1097/cnd.0000000000000047
- Minerbi A, Gonzalez E, Brereton NJ, Anjarkouchian A, Dewar K, Fitzcharles MA, et al. Altered microbiome composition in individuals with fibromyalgia. Pain. 2019;160(11):2589-2602. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001640
- Perrotta G. The intestinal microbiota: towards a multifactorial integrative model. Eubiosis and dysbiosis in morbid physical and psychological conditions. Arch Clin Gastroenterol. 2021;7(2):024-035. Available from: https://doi.org/10.17352/2455-2283.000094
- Perrotta G. Intestinal dysbiosis: definition, clinical implications, and proposed treatment protocol (Perrotta Protocol for Clinical Management of Intestinal Dysbiosis, PID) for the management and resolution of persistent or chronic dysbiosis. Arch Clin Gastroenterol. 2021;7(2):056-063. Available from: https://doi.org/10.17352/2455-2283.000100
- Perrotta G. Il microbiota intestinale nella pratica clinica. LK Ed.; 2022.
- O’Mahony LF, Srivastava A, Mehta P, Ciurtin C. Is fibromyalgia associated with a unique cytokine profile? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(6):2602-2614. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab146
- Perrotta G. Fibromyalgia (FM): definition, differential diagnosis, clinical contexts, and therapeutic approaches. The recent state of the medical art and a possible key to etiological interpretation. A narrative review: in the process of publication.
- Müller W, Schneider EM, Stratz T. The classification of fibromyalgia syndrome. Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(11):1005-10. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0403-9
- Perrotta G. Perrotta Integrative Clinical Interviews 3 (PICI-3): Development, regulation, updation, and validation of the psychometric instrument for the identification of functional and dysfunctional personality traits and diagnosis of psychopathological disorders, for children (8-10 years), preadolescents (11-13 years), adolescents (14-18 years), adults (19-69 years), and elders (70-90 years). Ibrain. 2024;146-163. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12148
- Manojlovic D, Kopse EV. The effectiveness of aerobic exercise for pain management in patients with fibromyalgia. Eur J Transl Myol. 2023;33(3):11423. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2023.11423
- Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(12):2281-3. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-1239
- Calandre EP, Hidalgo-Tallon J, Molina-Barea R, Rico-Villademoros F, Molina-Hidalgo C, et al. The Probiotic VSL#3® Does Not Seem to Be Efficacious for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Symptomatology of Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(10):1063. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101063
- Bonard R, Deambrogio V, Oliaro A. Interpretazione dei dati di laboratorio. 5th ed. Minerva Medica Ed.; 2005.
- Bulkley GB. Free radicals and other reactive oxygen metabolites: clinical relevance and the therapeutic efficacy of antioxidant therapy. Surgery. 1993;113(5):479-83. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8488463/
- Fogelholm M, Kukkonen-Harjula TK, Sievänen HT, Oja P, Vuori IM. Body composition assessment in lean and normal weight young women. Br J Nutr. 1996;75(6):793-802. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1079/bjn19960186
- Fogelholm M, von Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Westerterp KR. Assessment of fat mass during weight reduction in obese women. Metabolism. 1997;46(8):968-75. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90089-5
- Mazariegos M, Kral JG, Wang J, Waki M, Heymsfield SB, Pierson RN, et al. Body composition and surgical treatment of obesity. Effects of weight loss on fluid distribution. Ann Surg. 1992;216(1):69-73. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-199207000-00010
- Westerterp KR, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Wouters L. The Maastricht protocol for the measurement of body composition and energy expenditure with labeled water. Obes Res. 1995;3 Suppl 1:49-57. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1550-8528.1995.tb00007.x
- Montenero AS. Toxicity and tolerance of tryptophan and its metabolites. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol. 1978;32(5-6):188-94. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/583200/
- Cozzolino G, Dominici G, Latini P, Milia U. Urinary elimination of some metabolites of tryptophan along the nicotinic acid 'pathway' in normal subjects before and after administration of the amino acid. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1968;44(3):173-7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5687955/
- Davidson M, Rashidi N, Nurgali K, Apostolopoulos V. The Role of Tryptophan Metabolites in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9968. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179968
- Cervenka I, Agudelo LZ, Ruas JL. Kynurenines: Tryptophan's metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science. 2017;357(6349):eaaf9794. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf9794
- Ala M. Tryptophan metabolites modulate inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer by affecting immune system. Int Rev Immunol. 2022;41(3):326-345. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/08830185.2021.1954638
- Wilson DD. Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests. McGraw-Hill; 2007.
- Japanjac M, Milkovic L, Zarkovic N, Zarkovic K. Oxidative stress and regeneration. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;181:154-165. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.02.004
- Tan BL, Norhaizan ME, Liew WP-P. Nutrients and Oxidative Stress: Friend or Foe? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:9719584. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9719584
- Pisoschi AM, Pop A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;97:55-74. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040
- Horàk V. Vitamin D deficiency and its health effects. Vnitr Lek. 2019;65(11):724-727. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31906679/
- Gao H, Zhang Y, Liu K, Fan R, Li Q, Zhou Z. Dietary sodium butyrate and/or vitamin D3 supplementation alters growth performance, meat quality, chemical composition, and oxidative stability in broilers. Food Chem. 2022;1(390):133138. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133138
- Perrotta G. The new Dysfunctional Personality Model of the Anxiety Matrix (DPM-AM): “Neurotic Personality Disorder” (NPD). Ann Psychiatry Treatm. 2022;6(1):001-012. Available from: https://doi.org/10.17352/apt.000038
- Perrotta G. The new Dysfunctional Personality Model of the Dramatic Matrix (DPM-DM) and the Psychotic Matrix (DPM-PM): “Dramatic Personality Disorder” (DPD) and “Psychotic Personality Disorder” (PPD). Psychology and Mental Health Care. 2024;8(8). Available from: https://doi.org/10.31579/2637-8892/308
- Perrotta G. Maladaptive stress: Theoretical, neurobiological and clinical profiles. Arch Depress Anxiety. 2021;7(1):001-007. Available from: https://doi.org/10.17352/2455-5460.000057
- Perrotta G. Panic Disorder: Definitions, Contexts, Neural Correlates and Clinical Strategies. Curr Tr Clin & Med Sci. 2019;1(2):2019.CTCMS.MS.ID.000508. Available from: https://irispublishers.com/ctcms/fulltext/panic-disorder-definitions-contexts-neural-correlates-and-clinical-strategies.ID.000508.php
- Perrotta G. Depressive disorders: Definitions, contexts, differential diagnosis, neural correlates and clinical strategies. Arch Depress Anxiety. 2019;5(2):9-33. Available from: https://www.neuroscigroup.us/articles/ADA-5-138.pdf
- Benlidayi IC. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis and treatment of fibromyalgia. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(5):781-791. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04251-6
- Ege F, Isik R. A Comparative Assessment of the Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Fibromyalgia under Duloxetine Treatment. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(8):161. Available from: https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2808161
- Yao M, Wang S, Han Y, Zhao H, Yin Y, Zhang Y, et al. Micro-inflammation related gene signatures are associated with clinical features and immune status of fibromyalgia. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):594. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-023-04477-w
- Khamisy-Farah R, Fund E, Raibman-Spector S, Adawi M. Inflammatory Markers in the Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia. Isr Med Assoc J. 2021;23(12):801-804. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34954920/
- Mendieta D, De la Cruz-Aguilera DL, Barrera-Villalpando MI, Becerril-Villanueva E, Arreola R, Hernández-Ferreira E, et al. IL-8 and IL-6 primarily mediate the inflammatory response in fibromyalgia patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2016;290:22-5. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.11.011
- Ataoglu S, Ankarali H, Samanci R, Ozsahin M, Admis O. The relationship between serum leptin level and disease activity and inflammatory markers in fibromyalgia patients. North Clin Istanbul. 2018;5(2):102-108. Available from: https://doi.org/10.14744/nci.2017.31644
- Zabihiyeganeh M, Kadijani AA, Akbari A. Association of serum vitamin D status with serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and clinical severity of fibromyalgia patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023;55:71-75. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.03.006
- Horta-Baas G, Romero-Figueroa MDS. Clinical utility of red blood cell distribution width in inflammatory and non-inflammatory joint diseases. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22(1):47-54. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185x.13332
- Wang Y, Wei J, Zhang W, Doherty M, Zhang Y, Xie H, et al. Gut dysbiosis in rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 92 observational studies. EBioMedicine. 2022;80:104055. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104055
- Molina F, Del Moral ML, La Rubia M, Blanco S, Carmona R, Rus A. Are Patients With Fibromyalgia in a Prothrombotic State? Biol Res Nurs. 2019;21(2):224-230. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/1099800418824716
- Ranzolin A, Branco Pinto Duarte AL, Bredemeier M, da Costa Neto CA, Ascoli BM, Wollenhaupt-Aguiar B, et al. Evaluation of cytokines, oxidative stress markers, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with fibromyalgia - A controlled cross-sectional study. Cytokine. 2016;84:25-8. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2016.05.011
Article Alerts
Subscribe to our articles alerts and stay tuned.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 Save to Mendeley
Save to Mendeley
